
The General table in the uplink carrier node enables you to turn the uplink carrier on and off, select a saved channel configuration, and view the length of the generated waveform.
Additional parameter setup tables for the advanced uplink carrier are described in Baseband (Advanced LTE-A FDD Uplink) and Fading contained in Waveform (multipath only) (Advanced LTE-A FDD Uplink).

Double-click or use the drop-down menu to turn the carrier Off or On.
Select a channel configuration with the desired modulation type, bandwidth, and number of resource blocks (RB) from the drop-down list. This parameter is not available for LTE-A Pro.
The User Defined setting is not selectable until certain parameters are changed (e.g. in the Component Carrier node: State, Auto Symbol Rolloff Length Configuration, Baseband Filter; and in the Uplink node: Total Number of Antennas, System Bandwidth, ...) then User Defined is automatically set by the software.
Range: 10 to 160 ms (Multicarrier)
Default: 10 (ms)
Enter a value in milliseconds for Waveform Generation Length. Total Sample Points is based on the selected Waveform Generation Length and Oversampling Ratio as shown below:
Total Sample Points = Base Sampling Rate (MHz) × Oversampling Ratio × 1000 × Waveform Generation Length (ms)
If the Waveform Generation Length parameter is set less than the Transmission Configuration Length, the value of Transmission Configuration Length is changed to be ≤Waveform Generation Length. In summary, the relation between Transmission Configuration Length and Waveform Generation Length is that the Transmission Configuration Length ≤Waveform Generation Length. (For more information on the Transmission Configuration Length parameter refer to the Channel Setups Advanced LTE FDD UL and DL topics.)
While the long waveform is playing, the following signal or data values are generated sequentially.
Uplink:
HARQ Process scheme in UL-SCH is automatically updated until the end of the waveform.
Payload data in UL-SCH is sequentially used for transport block until the end of the waveform.
Figure 1 shows the generic frame structure.
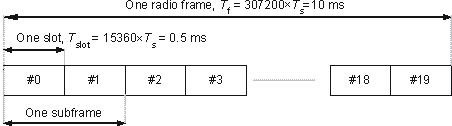
Figure 1. Generic radio frame structure